Table of Contents
Supply chain logistics is experiencing a new wave of digitalization. The integration of emerging technologies is not only enhancing operational efficiency but also driving sustainability and resilience across various industries.
The term “digitalization” describes the application of digital technologies to support both creative and current freight transportation and logistics management and provision.
Technological advancements such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, 5G, blockchain, data analytics, pervasive computing, and autonomous technology are evolving rapidly. These innovations are reshaping supply chain management, a shift accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic. Changes in customer expectations and consumer behavior, driven by easy access to information, e-commerce, and digital services, have further transformed the industry.
For instance, AI and machine learning are revolutionizing demand forecasting and inventory management. Companies like UPS have implemented AI-driven systems such as ORION, which optimizes delivery routes to save over 10 million miles annually, leading to significant cost reductions and improved service levels. Similarly, DHL employs predictive analytics to enhance operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Blockchain technology is gaining traction for its ability to provide a secure and transparent record of transactions across the supply chain. Walmart has successfully utilized blockchain to trace food products from farm to store, ensuring safety and compliance while reducing recall times. This decentralized ledger not only enhances traceability but also fosters trust among stakeholders by preventing fraud.
Moreover, robotics and automation are transforming warehousing operations. Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) and robotic arms streamline picking and packing processes, allowing companies like Amazon to handle high volumes of orders with increased speed and accuracy. The MHI Annual Industry Report (2023) indicates that nearly 80% of logistics companies plan to invest in automation technologies in the coming years.
New business models, such as logistics-as-a-service and mobility-as-a-service, have emerged due to digitalization. These models are supported by innovations like micro-fulfillment centers, cryptocurrency, and the Internet of Things (IoT).
The stakes are high. According to a McKinsey report, companies that adopt digital supply chain technologies can expect up to a 30% increase in operational efficiency while reducing costs by up to 20%.
This article breaks down the top emerging supply chain logistics technologies transforming the industry.
Emerging Supply Chain Logistics Technologies
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
- Blockchain Technology
- Internet of Things (IoT)
- Autonomous Vehicle Technology and Drones
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
- Digital Twins
- Big Data and Advanced Analytics
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) into supply chain management is revolutionizing the way businesses operate. These technologies enhance decision-making, optimize processes, and improve overall efficiency. Let’s face it, organizations are increasingly relying on data-driven insights, and AI and ML are becoming indispensable tools for solving modern supply chains demands.
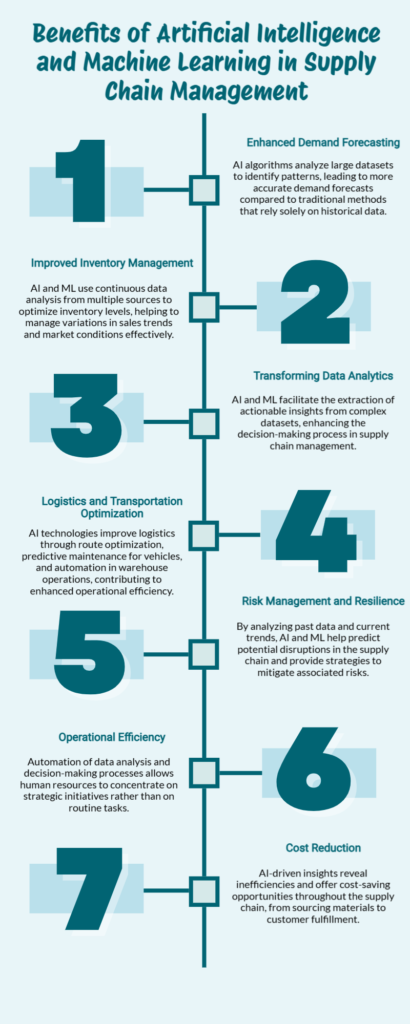
Enhanced Demand Forecasting
One of the most significant impacts of AI and ML in supply chain management is in demand forecasting. Traditional forecasting methods often rely on historical data and can be prone to inaccuracies. In contrast, AI algorithms analyze vast datasets to identify patterns and trends, enabling more accurate predictions. For instance, companies utilizing AI-driven demand forecasting have reported a 35% reduction in inventory levels while improving service levels by up to 65%. This enhanced accuracy helps organizations maintain optimal inventory levels, reducing the risk of stockouts or overstock situations.
Improved Inventory Management
AI and ML also play a crucial role in inventory management. By continuously analyzing data from various sources—such as sales trends, seasonal fluctuations, and market conditions—these technologies enable businesses to optimize stock levels across their supply chains. For example, machine learning algorithms can automate inventory replenishment processes, ensuring that products are restocked just in time to meet customer demand without tying up excess capital in unsold goods. This automation not only accelerates operations but also minimizes human error, enhancing overall reliability.
Transforming Data Analytics
AI and ML excel in extracting actionable insights from vast datasets, a task that is increasingly complex and critical in modern supply chain management. By processing data from various sources – including supplier performance, customer feedback, and real-time market trends – these technologies provide a nuanced understanding of the supply chain dynamics.
Logistics and Transportation Optimization
In logistics, AI and ML offer route optimization, predictive maintenance for transportation vehicles, and automated warehousing operations. These technologies can dynamically adjust routes in real-time based on traffic conditions, weather, and delivery urgency, ensuring optimal delivery schedules. For example, companies like UPS have implemented AI-driven systems such as ORION, which optimizes delivery routes to save over 10 million miles annually, leading to significant cost reductions and improved service levels.
Risk Management and Resilience
The global market is increasingly volatile, therefore, effective risk management is critical for supply chain resilience. AI and ML enable organizations to identify potential vulnerabilities within their supply chains proactively. By analyzing historical data and current market conditions, these technologies can forecast disruptions—such as supplier failures or natural disasters—and recommend strategies to mitigate risks. This proactive approach allows businesses to build more robust supply chains capable of adapting to unexpected challenges.
Operational Efficiency
AI and ML contribute significantly to operational efficiency. Automated data analysis and decision-making free up human resources to focus on strategic tasks. For instance, AI-driven chatbots and automated customer service tools can handle routine inquiries, while human staff address more complex customer needs.
Cost Reduction
The cost-saving potential of AI and ML in supply chain management is substantial. By optimizing stock levels, reducing waste, and improving transportation efficiency, businesses can achieve significant financial savings. AI-driven analytics can also identify inefficiencies and cost-saving opportunities across the supply chain, from procurement to customer delivery.
Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology is revolutionizing supply chain management by enhancing transparency, traceability, and efficiency. Businesses are facing increasing pressure to improve operational performance and respond to consumer demands for accountability, and blockchain offers a robust solution that addresses many traditional challenges in supply chains. Let’s explore some of them.
Enhancing Transparency
One of the most significant advantages of blockchain technology in supply chain management is its ability to provide unprecedented transparency. Blockchain operates as a decentralized ledger that records all transactions in a secure and immutable manner. This transparency allows stakeholders to view the entire history of a product from its origin to its final destination.
- Real-Time Tracking: By integrating blockchain with IoT devices such as RFID tags and smart sensors, companies can monitor the conditions of goods throughout their journey. For instance, temperature-sensitive products like pharmaceuticals can be tracked to ensure they remain within required temperature ranges during transport, reducing the risk of spoilage or contamination.
- Visibility Across the Supply Chain: According to a KPMG survey, 87% of respondents identified supply chain visibility as a key operational priority in 2023. Blockchain facilitates this visibility by providing all parties access to the same data in real-time, thereby minimizing miscommunication and errors.
Improving Traceability
Traceability is critical in supply chain management, particularly for industries where product authenticity is paramount. Blockchain technology enhances traceability by allowing companies to track products at every stage of the supply chain.
- Provenance Tracking: Blockchain enables businesses to verify the origin and journey of their products. For example, companies like Walmart have implemented blockchain solutions to trace food products back to their source farms, improving food safety and compliance with regulations.
- Counterfeit Prevention: The immutable nature of blockchain records helps prevent fraud and counterfeiting. For instance, luxury brands are increasingly using blockchain to authenticate their products, ensuring that consumers receive genuine items rather than counterfeit goods.
Increasing Efficiency
Blockchain technology streamlines operations by automating processes and reducing administrative overhead.
- Smart Contracts: These self-executing contracts automatically enforce and execute terms when predefined conditions are met. This automation reduces the need for intermediaries and accelerates transaction processes. For example, a shipping company could automatically release payment upon confirmation of delivery through blockchain verification.
- Cost Reduction: By eliminating intermediaries and reducing paperwork, blockchain can lead to significant cost savings. The global market for blockchain in supply chain management is projected to grow from $2.08 billion in 2024 to $9.77 billion by 2030, reflecting an impressive compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 29.14%.
Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) provides unprecedented levels of visibility, control, and efficiency in supply chain logistics. By connecting various devices and systems, IoT enables real-time data collection and analysis, allowing companies to optimize their operations, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction. This transformation is evident in various applications across the logistics landscape, from tracking shipments to managing inventory and improving overall supply chain resilience.
Real-Time Tracking and Monitoring
One of the most significant impacts of IoT on supply chain logistics is the ability to track shipments in real time. IoT devices such as GPS trackers and RFID tags provide continuous monitoring of cargo, enabling logistics managers to know the exact location and condition of their goods at all times. For instance, Amazon employs a fleet of IoT-enabled robots in its warehouses to scan packages and track inventory levels accurately. This system not only streamlines warehouse operations but also ensures that products are readily available for timely delivery.
Enhanced Predictive Analytics
IoT technology empowers supply chain managers with predictive analytics capabilities that allow them to foresee potential disruptions and take proactive measures. Companies collect data from various sources—such as weather forecasts, traffic conditions, and historical shipment data—helping them identify patterns and anticipate issues before they escalate. For example, Nissan employs IoT solutions to link its multiple industrial units, enabling better forecasting of demand and supply fluctuations across its global operations.
Improved Operational Efficiency
The integration of IoT devices into logistics operations leads to improved efficiency across the supply chain. Automated systems can trigger alerts for low inventory levels or damaged goods, allowing for swift corrective actions. IoT sensors can automatically notify warehouse managers when stock falls below predefined thresholds or when products are exposed to harmful conditions during transport.
Autonomous Vehicle Technology and Drones
Autonomous vehicle technology has profoundly transformed the logistics and supply chain sectors. These vehicles, which include self-driving trucks, drones, and automated delivery systems, promise to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve safety across global supply chains.
A study utilizing simulation frameworks demonstrated that Connected and Autonomous Vehicles (CAVs) could decrease total travel time by up to 20% while also reducing greenhouse gas emissions significantly. A simulation conducted involving the fresh potato supply chain revealed that increased CAV market penetration could lead to lower supply chain costs due to faster transit times.
Final Mile Delivery Innovations
The final mile of delivery is often the most challenging and costly segment of the supply chain. Companies like Starsky Robotics are experimenting with remote-controlled autonomous trucks that can operate without drivers during highway travel.
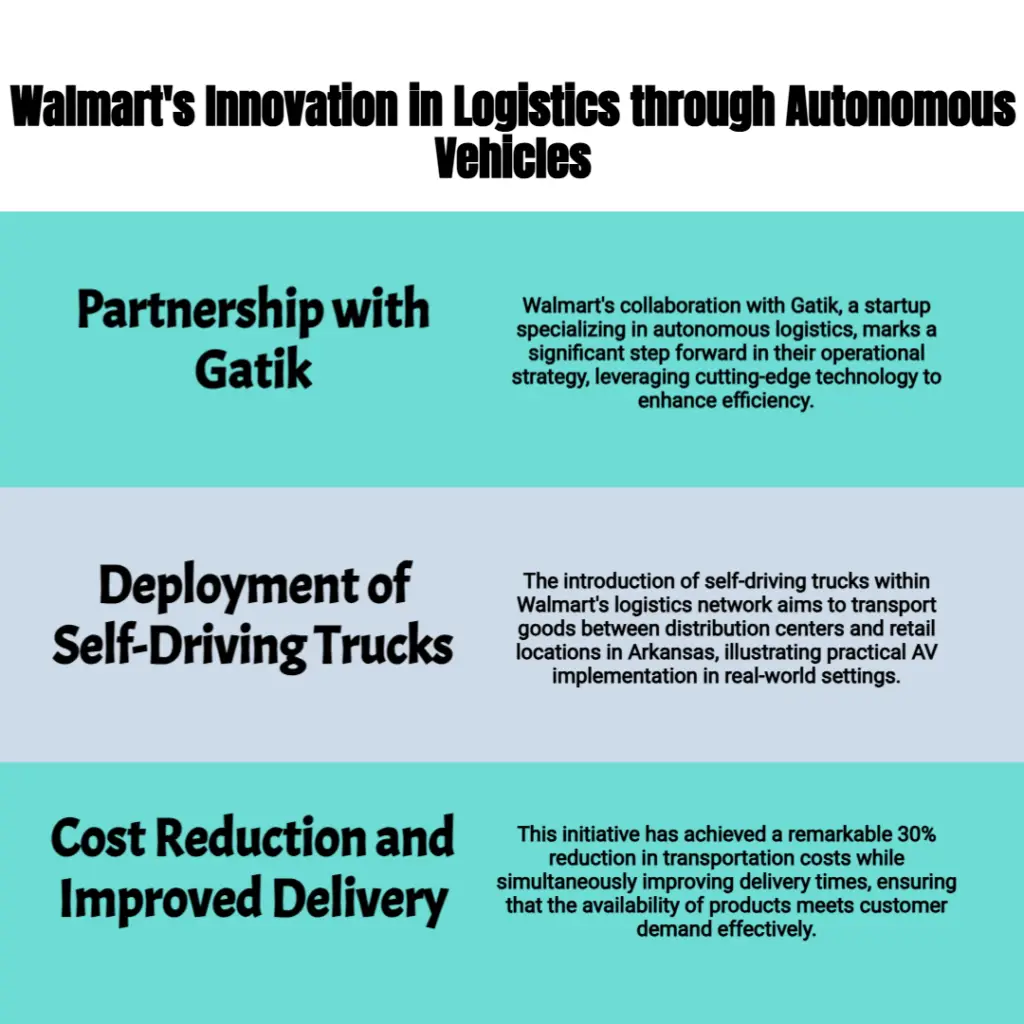
Walmart has been at the forefront of integrating AV technology into its logistics strategy. The retail giant partnered with Gatik, a startup focused on autonomous middle-mile logistics. Together, they deployed self-driving trucks to transport goods between distribution centers and retail locations in Arkansas. This initiative has resulted in a 30% reduction in transportation costs while improving delivery times by ensuring consistent product availability.
Robotics Process Automation (RPA)
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is rapidly reshaping the logistics and supply chain industry by automating repetitive, rule-based tasks traditionally performed by humans. This technology utilizes software robots to execute processes with speed and accuracy, significantly enhancing operational efficiency and reducing costs. As supply chains become increasingly complex, RPA emerges as a critical tool for organizations aiming to streamline their operations and improve service delivery.
RPA is particularly well-suited for logistics due to the high volume of repetitive tasks involved in supply chain management. These tasks often include order processing, inventory management, shipment tracking, invoicing, and customer service interactions. Automating manual tasks reduces labor costs and operational expenses. Companies can save significant amounts by reallocating resources to more strategic activities.
Walmart is one company that has embraced RPA to streamline various aspects of its supply chain management. The retail giant utilizes over 500 bots for tasks ranging from inventory management to HR processes. DHL has integrated RPA into its logistics operations to enhance efficiency and accuracy in order processing and shipment tracking.
Digital Twins
A Digital Twin is a digital representation of a physical object or system that mirrors its real-time status, behavior, and performance. This capability allows for enhanced monitoring, predictive maintenance, scenario simulation, and process optimization.
Key Applications of Digital Twins in Logistics
1. Real-Time Tracking and Monitoring
One of the most significant advantages of Digital Twins is the ability to track shipments and assets in real time. For example, IBM has developed a Digital Twin system that utilizes sensor data to create virtual models of inventory. This system allows companies to monitor location, condition (such as temperature and humidity), and other critical parameters for sensitive goods like pharmaceuticals and perishables.
2. Predictive Maintenance
Digital Twins facilitate predictive maintenance by analyzing data from sensors installed in logistics assets such as trucks and warehouse equipment. For instance, Maersk has implemented Digital Twin technology to monitor the health of its shipping containers. They predict potential failures before they occur, helping Maersk significantly reduced downtime and maintenance costs while enhancing overall fleet performance
3. Warehouse Optimization
Digital Twins can create a virtual model of a warehouse, helping logistic managers simulate various configurations to identify the most efficient layouts. This capability allows companies to experiment with different setups without incurring costly physical alterations.
Vita Coco utilized RELEX’s digital twin technology to optimize its supply chain planning process, resulting in millions of dollars in cost savings through improved sourcing and distribution planning.
Big Data and Advanced Analytics
Big data and advanced analytics is transforming the logistics and supply chain industry. These technologies enable organizations to harness vast amounts of data generated throughout the supply chain, transforming operations, enhancing decision-making, and improving customer satisfaction.
Big data refers to the massive volume of structured and unstructured data generated from various sources, including IoT sensors, GPS trackers, transaction records, and customer interactions. In logistics, companies can leverage this data to gain insights that drive operational efficiency and strategic decision-making.
Key Benefits of Big Data in Logistics:
- Enhanced Operational Efficiency
Real-time monitoring and predictive analytics enable companies to identify inefficiencies in their operations. Companies like DHL use big data analytics to optimize their delivery routes, resulting in a reported 20% reduction in transportation costs through improved route planning.
- Improved Visibility and Transparency
Advanced analytics tools provide unprecedented visibility into supply chain processes. Companies can track shipments in real-time and monitor inventory levels effectively.
- Demand Forecasting
Amazon utilizes sophisticated algorithms powered by big data to forecast demand for products accurately, enabling it to optimize inventory levels and reduce stockouts.
- Cost Reduction
Big data analytics helps companies identify areas where costs can be minimized. For example, Unilever has implemented big data strategies that have led to a 10% reduction in logistics costs by optimizing transportation routes and warehousing strategies.
Conclusion
According to a report by Allied Market Research, the “supply chain management market” was valued at $27.2 billion in 2022, and is projected to reach $85.3 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 11.1% from 2023 to 2033. This has been heavily bolstered by digitalization.
Emerging supply chain logistics technologies are more than just trends; they are reshaping the industry’s future. Businesses that adopt these innovations can achieve unparalleled efficiency, cost savings, and customer satisfaction. From AI-driven forecasting to blockchain-enhanced transparency, the supply chain landscape is ripe with opportunities for growth and innovation.
As these technologies continue to evolve, companies that prioritize digital transformation will be best positioned to thrive in an increasingly competitive global market.













