Table of Contents
A few years ago, autonomous logistics was considered a futuristic fantasy, but that’s no longer the case. These days, autonomous vehicles (AVs) are transforming supply chain logistics, offering never-seen-before efficiency, cost savings, and safety enhancements. From self-driving trucks to automated drones and warehouse robots, AVs are reshaping how goods are transported and managed.
Think of a world where orders are delivered faster than ever, trucks never need rest stops, and warehouses operate with robotic precision 24/7. Yes, that’s currently our reality.
For decades, supply chain logistics has relied on human-driven trucks, manual warehouse operations, and traditional delivery systems. But the industry is facing serious challenges: driver shortages, rising fuel costs, safety concerns, and increasing demand for faster deliveries.
This is where autonomous vehicles excel. From self-driving trucks revolutionizing long-haul transport to AI-powered delivery drones dropping off packages at your doorstep, AVs are redefining efficiency in logistics. And this isn’t just a minor upgrade—it’s a game-changer that could cut transportation costs by 45% and reduce delivery times by half, according to a study by McKinsey.
But what does this shift really mean for businesses, consumers, and the global economy? And why aren’t we seeing fully autonomous fleets on every highway yet? Let’s dive into why autonomous vehicles are such a big deal in supply chain logistics and what the future holds for this groundbreaking technology.
Will Autonomous Trucks Replace Truckers?
From the look of things, autonomous trucks will not totally replace truck drivers. And here’s why. According to the American Trucking Associations (ATA), the U.S. alone faces a shortage of more than 80,000 truck drivers, a number that could double by 2030 if left unaddressed. Meanwhile, traditional and e-commerce orders are skyrocketing, putting even more pressure on logistics companies to keep up.
Impact of AVs on Supply Chain Efficiency
Autonomous vehicles (AVs) can significantly increase efficiency in supply chain logistics by reducing the need for human labor. They can be programmed to follow predetermined routes, enabling them to travel more quickly and efficiently than human-driven vehicles. This reduces the time and resources needed to complete deliveries, resulting in faster delivery times and lower costs. Moreover, AVs can be programmed to avoid traffic and other obstacles, further increasing efficiency.
Experts indicate that automation and AI are expected to be a leading trend in the logistics, transport, and supply chain sectors. The global market is predicted to exceed $600 billion by 2030. Within the logistics industry, autonomous vehicles could cut costs, address labor shortages, and improve overall performance.
A recent poll indicated that 66% of respondents believe automation and AI will dominate the logistics, transport, and supply chain sector in 2025. Also, experts predict that autonomous driving will enter the market around 2020-2025, with 75% of cars expected to be autonomous by 2035.
While the AV industry is still in its early stages, its potential for optimizing picking operations, transport route planning, and other aspects of logistics is nothing short of tremendous. Autonomous vehicles have the potential to bring revolutionary improvements to almost every node in the supply chain.
The Evolution of Autonomous Vehicles in Logistics
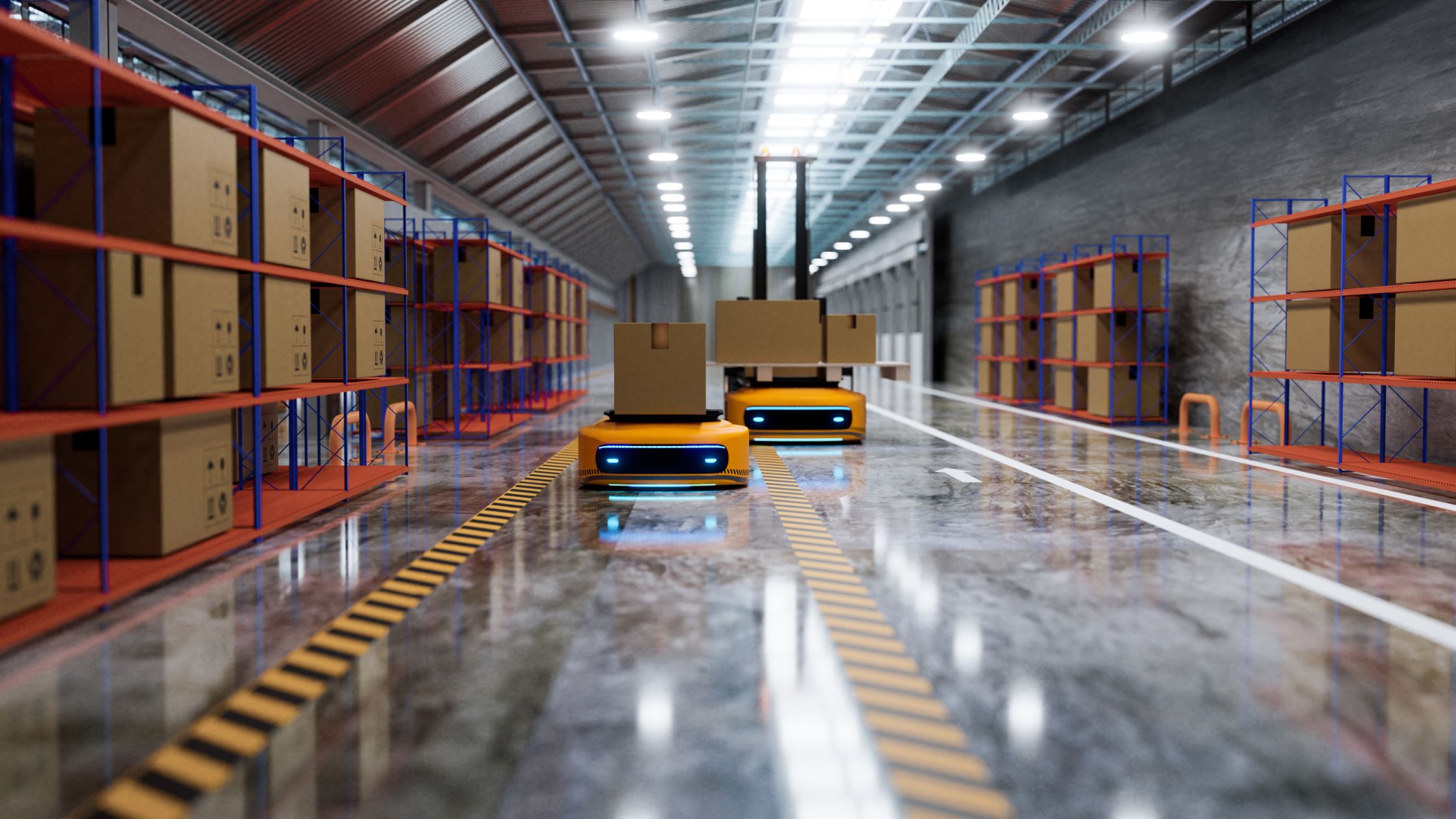
The integration of autonomous vehicles into logistics has evolved from early automation efforts to sophisticated, self-navigating systems. Initially, automation in logistics focused on mechanizing repetitive tasks within controlled environments, such as automated guided vehicles (AGVs) in warehouses. Today, advancements in AI and machine learning have enabled the development of autonomous trucks, drones, and delivery robots capable of navigating complex environments with minimal human intervention.
Companies like Aurora Innovation and Kodiak Robotics are pioneering the deployment of self-driving trucks for long-haul transportation, while firms such as Nuro are utilizing delivery robots for last-mile solutions.
These AVs are operating at Level 4 and Level 5 automation.
According to the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), there are 6 levels of driving automation:
- Level 0: No automation. The human driver performs all driving tasks.
- Level 1: Driver Assistance. The vehicle can control either steering or acceleration/deceleration using information about the driving environment, with the human driver performing all remaining aspects of the dynamic driving task.
- Level 2: Partial Automation. The vehicle has combined automated functions like acceleration and steering, but the human driver must remain engaged with the driving task and monitor the environment at all times.
- Level 3: Conditional Automation. The vehicle can perform all aspects of the driving task under certain conditions. The human driver must be ready to take back control when requested by the vehicle.
- Level 4: High Automation. The vehicle can perform all driving tasks and monitor the driving environment in certain circumstances. The human driver has the option to control the vehicle.
- Level 5: Full Automation. The vehicle is capable of performing all driving tasks, under all conditions, without any human intervention.
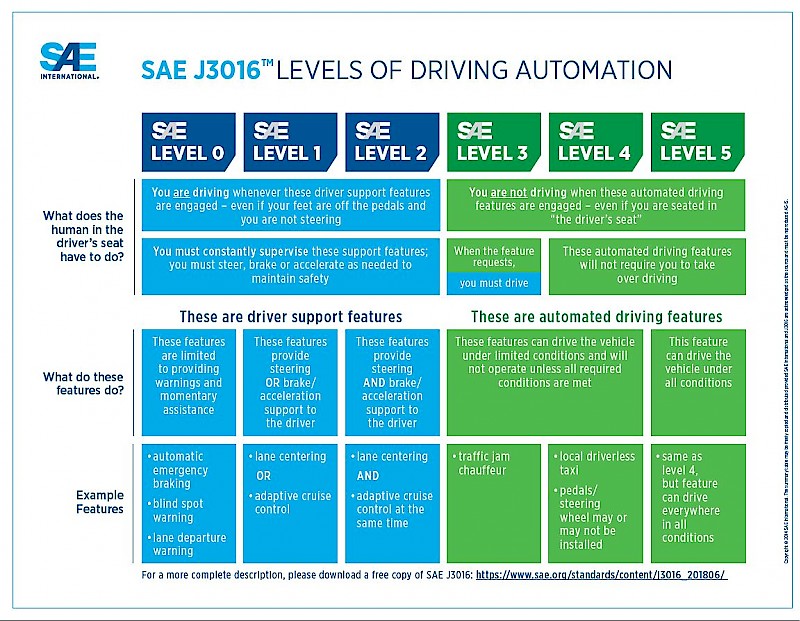
Companies like Kodiak Robotics, Gatik, and Aurora Innovation are operating at Level 4 and Level 5 driving automation, a resounding accomplishment because autonomous vehicles were dismissed as something out of a sci-fi movie just a few years ago.
Types of Autonomous Vehicles in Logistics
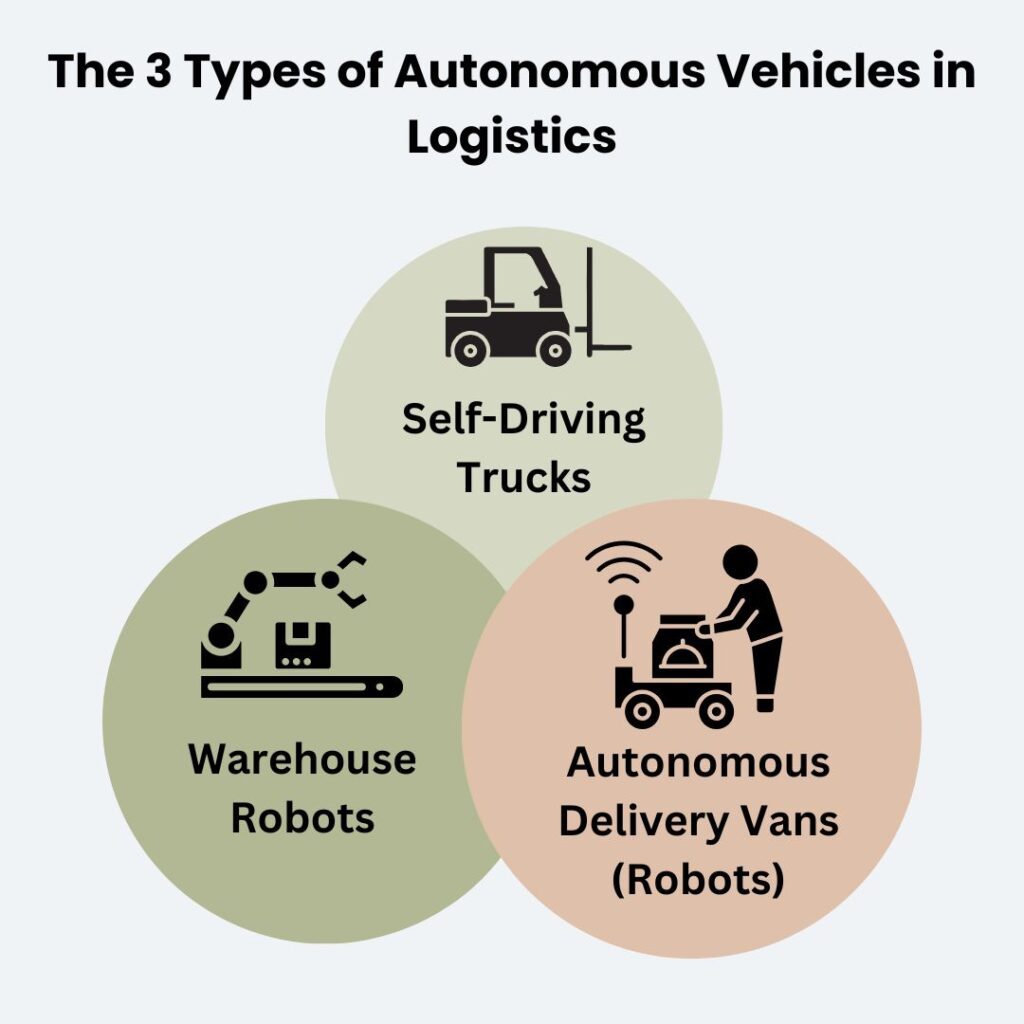
- Self-Driving Trucks
Designed for long-haul routes, self-driving trucks operate with advanced sensors and AI to navigate highways, reducing the need for human drivers. For instance, Aurora Innovation has been testing autonomous freight deliveries, aiming to improve efficiency and safety in long-distance trucking.
- Autonomous Delivery Vans (Robots)
Used for urban deliveries, these vehicles handle last-mile logistics, ensuring timely and efficient delivery to consumers. Companies like Starship Technologies have developed autonomous delivery vans that transport groceries and small packages in urban settings.
- Warehouse Robots
Autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) and AGVs are employed within warehouses to manage inventory, transport goods, and assist in order fulfillment. For example, Amazon utilizes robots in its fulfillment centers to streamline operations and increase efficiency.
You may Also Like:
Top 5 Leading Autonomous Trucking Companies Powering Autonomous Logistics (2025)
Benefits of Autonomous Vehicles in Supply Chain Logistics
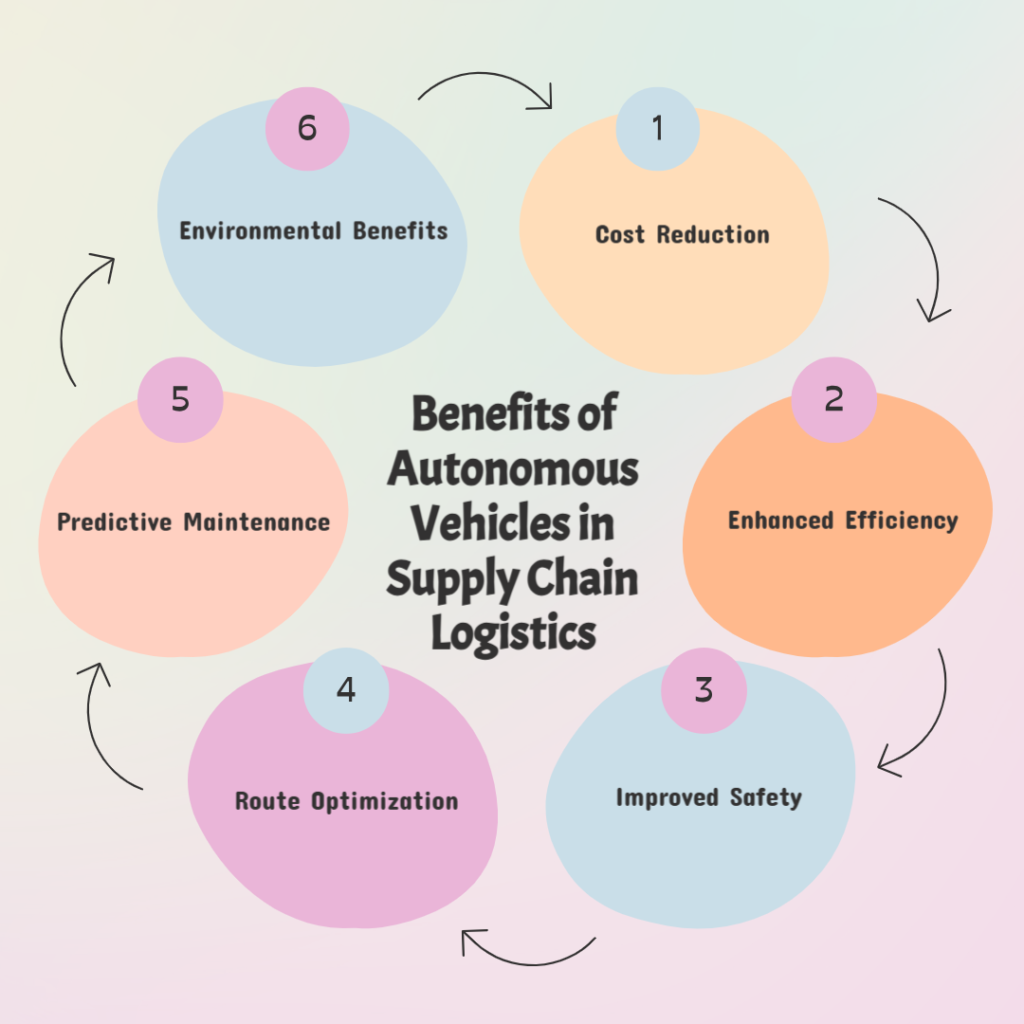
- Cost Reduction: AVs can significantly lower labor costs by reducing reliance on human drivers and workers. A study by McKinsey suggests that autonomous delivery vehicles could reduce delivery costs by up to 40%.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Autonomous vehicles can operate 24/7 without fatigue, leading to faster delivery times and increased throughput. In warehouse settings, robots can continuously manage inventory and fulfill orders, reducing processing times.
- Improved Safety: By eliminating human error, AVs have the potential to reduce accidents in transportation. Autonomous trucks are equipped with advanced sensors and AI systems that enhance safety by monitoring surroundings and making real-time decisions.
- Route Optimization: Autonomous systems can process vast amounts of data in real-time, allowing for dynamic route optimization based on traffic conditions, weather, and other variables. This leads to faster delivery times and less congestion.
- Predictive Maintenance: With sensors and AI, AVs can predict when maintenance is needed, reducing unexpected vehicle downtime and ensuring that vehicles are always in optimal condition for transport.
- Scalability: Businesses can scale operations more readily without the need to recruit and train additional human drivers, allowing for growth in delivery capacity without proportional increases in labor costs.
- Environmental Benefits: Many autonomous vehicles are electric, contributing to reduced carbon emissions. Optimized routing and efficient driving patterns further decrease fuel consumption, supporting sustainability initiatives.
The Role of 5G and IoT in Autonomous Logistics
For autonomous vehicles to operate safely and efficiently, they must constantly communicate with other vehicles, traffic systems, and logistics hubs. Traditional 4G networks simply don’t have the speed or low latency required for real-time coordination at scale. That’s why 5G is a game-changer in autonomous logistics.
5G enables real-time vehicle–to-vehicle and vehicle-to-infrastructure communication. With ultra-low latency (as low as 1 millisecond) and data speeds 100 times faster than 4G, 5G networks allow autonomous trucks, drones, and robots to communicate instantly, making split-second decisions to avoid collisions, optimize routes, and adapt to changing road conditions.
For example, Einride, a Swedish autonomous trucking company, relies on 5G-powered remote monitoring to manage its fleet of electric self-driving trucks. In the event of unexpected obstacles, remote operators can take control of a truck in real time, ensuring uninterrupted operations. Similarly, Verizon and UPS have been testing 5G-enabled drone deliveries, reducing delays caused by network lags and improving last-mile logistics efficiency.
IoT plays a crucial role in tracking goods, monitoring vehicle performance, and optimizing fleet operations. Connected sensors embedded in trucks, warehouses, and cargo containers continuously collect and transmit real-time data, helping logistics managers make data-driven decisions.
A great example of IoT-driven logistics is DHL’s SmartSensor technology, which helps monitor shipments in real time, alerting operators if a package is exposed to extreme temperatures or mishandling.
You May Also Like:
Top 7 Leading Autonomous Delivery Companies (2025)
Autonomous Vehicles the First Multitrillion-Dollar Robotics Industry?
The CEO of Nvidia, Jensen Huang, during his keynote address at CES 2025 opined that autonomous vehicles will be the first multitrillion-dollar robotics industry. An extremely bold prediction considering the fact that autonomous vehicles haven’t fully attained mainstream utility.
Huang’s statement underscores the significant role AVs are expected to play in reshaping numerous sectors, with logistics and supply chain operations standing out as primary beneficiaries. Huang’s vision is rooted in the transformative potential of autonomous technology to streamline and enhance the efficiency of transportation networks, which are fundamental to global commerce.
The impact on supply chain and logistics operations is profound. AVs promise to introduce unprecedented levels of efficiency by enabling 24/7 operations, cutting down on human error, and optimizing routes in real time.
Huang highlighted NVIDIA’s partnerships with autonomous trucking giants like Aurora Innovation and Continental (and Volvo), leveraging its DRIVE Hyperion AV Platform powered by the AGX Thor system-on-a-chip (SoC) – a new generation system for powering autonomous vehicles. Nvidia’s Drive Thor processor is 20 times faster than its predecessor, Nvidia Drive Orin.

Also, Nvidia’s Cosmos platform, which generates photo-realistic simulations for training AVs, will immeasurably help the development of these vehicles, making them more scalable and cost-effective.
By utilizing Nvidia’s state-of-the-art technology, AVs could dramatically alter warehouse-to-warehouse and last-mile delivery processes. Autonomous trucks can facilitate just-in-time delivery more effectively, reducing inventory holding costs and improving cash flow for businesses. In urban settings, smaller autonomous delivery vehicles or drones could take over, reducing congestion and the environmental footprint associated with traditional delivery methods.
Jensen Huang might not be far off from the truth; autonomous vehicles could, indeed, become the first multitrillion-dollar robotics industry.
Challenges to Adoption
Despite the advantages, several challenges hinder the widespread adoption of AVs in logistics and supply chain management:
- Regulatory Hurdles: Varying regulations across regions complicate the deployment of autonomous vehicles. Ensuring compliance with local laws and obtaining necessary approvals can be time-consuming and costly.
- Safety Concerns: Public trust in autonomous technology remains a significant factor. Many nurture fears of high-profile incidents involving self-driving vehicles. However, while these fears are valid, autonomous vehicle companies are undergoing rigorous safety validations to ensure their driverless operations are incident-free.
- Infrastructure Requirements: The successful deployment of AVs requires supportive infrastructure, such as smart roads and communication systems, which are not yet universally available.
- High Initial Investment: The development and integration of autonomous systems involve substantial capital expenditure, which may deter some companies from early adoption.
The Potential of Autonomous Vehicles to Reshape Supply Chain Logistics
Autonomous vehicles (AVs) have the potential to fundamentally reshape supply chain logistics, transforming how goods are transported, stored, and delivered. The shift towards automation is driven by advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), 5G connectivity, and the Internet of Things (IoT), enabling vehicles to operate with greater efficiency, precision, and reliability.
From long-haul trucking to last-mile deliveries, AVs promise to reduce costs, enhance safety, and improve supply chain resilience, marking a shift away from traditional logistics models.
One of the most immediate benefits of AVs in supply chain logistics is the ability to address labor shortages in the trucking industry. Autonomous trucks can help bridge this gap by handling long-haul routes that are often challenging for human drivers due to fatigue and regulatory restrictions on driving hours. Companies like Aurora Innovation and Kodiak Robotics are already testing autonomous freight networks, demonstrating that AVs can operate on major highways with no human intervention, potentially reducing delivery times and operating costs by up to 45%.
Last-mile logistics, which accounts for nearly 50% of total shipping costs in e-commerce, will be greatly impacted by self-driving vehicles. Autonomous delivery robots and drones can significantly reduce delivery expenses, enhance delivery speed, and reach remote areas where traditional couriers might struggle.
Companies like Amazon, Starship Technologies, and Nuro are leading the charge, deploying self-driving delivery vehicles that can navigate urban environments with high precision and minimal delays. This shift is particularly critical for industries such as pharmaceuticals and food delivery, where speed and reliability are paramount.
In the long run, the potential of autonomous vehicles to reshape supply chain logistics is undeniable. As AI, 5G, and IoT technologies continue to evolve, AVs will become an integral part of modern logistics, driving cost savings, operational efficiency, and sustainability. Companies that embrace this transformation early will gain a significant competitive edge, ensuring faster deliveries, lower costs, and greater adaptability in an increasingly digital world.
The future of supply chain logistics is autonomous, and the industry is on the brink of a revolution that will redefine global trade for decades to come.
You May Also Like:
Top 7 Emerging Supply Chain Logistics Technologies
Industry 4.0 in Supply Chains: Here’s How It Works
Top 10 Global Supply Chain Trends to Watch in 2025
Top 7 Leading Autonomous Delivery Companies (2025)
CES 2025: These Emerging Technologies Will Revolutionize Global Supply Chains













